

You must understand the functionality of an NIC card, and what a MAC address is for the CCNA exam. The first 3 bytes contain a manufacturer code, and the last 3 bytes contain a unique station ID. The highest possible hexadecimal number is FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF, which is a broadcast address. This is sometimes referred to as the Burned-In Address (BIA).Ī MAC address consists of six hexadecimal numbers. To avoid this confusion, MAC addresses, in most cases, are permanently burned into the NIC's memory. A packet intended for NIC #35 (a simplification of the MAC address) would not know to which NIC #35 it was destined. Obviously, it would be confusing if there were two or more NICs with the same MAC address. Each manufacturer of network cards is provided a unique set of MAC addresses so that (theoretically, at least) every NIC that is manufactured has a unique MAC address. The MAC address of an NIC is usually burned into a read-only memory (ROM) chip on the NIC. Every NIC has a unique MAC address, also called the physical address, which identifies that specific NIC on the network.
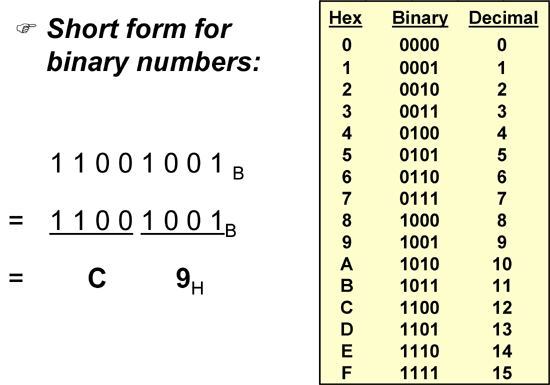
Physical addressing is addressed at the MAC sublayer. It is responsible for moving data packets from one NIC to another across a shared transmission medium such as an Ethernet or fiber-optic transmission medium. The MAC sublayer provides control for accessing the transmission medium.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
